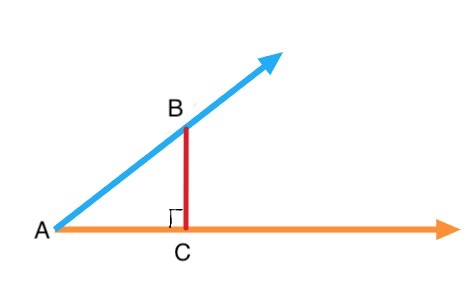
Right Triangle
Suppose we pick a random point `B` on the terminal side, and draw "straight down" to point `C` of the initial side, we get a right triangle `∆ABC`.
 Now Let us pick another random point `D` on the terminal side, and draw "straight down" to point `E` of the initial side, we get a right triangle `∆ADE`.
Now Let us pick another random point `D` on the terminal side, and draw "straight down" to point `E` of the initial side, we get a right triangle `∆ADE`.
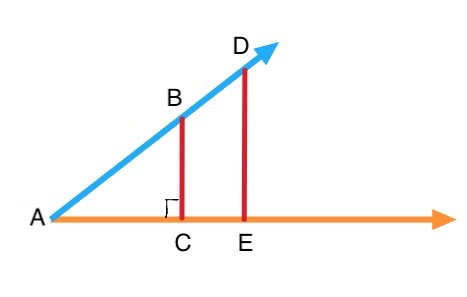 `∆ABC` and `∆ADE` are similar.
Property of similar triangle:
`(AB)/(AD) = (BC)/(DE) = (AC)/(AE)`
From this property we can get:
`(DE)/(AD) = (BC)/(AB)`
In other words, the ratio of the opposite side of `angle A` to the hypotenuse is a constant.
Mathematicians named this ratio sine(`sin`)
`∆ABC` and `∆ADE` are similar.
Property of similar triangle:
`(AB)/(AD) = (BC)/(DE) = (AC)/(AE)`
From this property we can get:
`(DE)/(AD) = (BC)/(AB)`
In other words, the ratio of the opposite side of `angle A` to the hypotenuse is a constant.
Mathematicians named this ratio sine(`sin`)
 Now Let us pick another random point `D` on the terminal side, and draw "straight down" to point `E` of the initial side, we get a right triangle `∆ADE`.
Now Let us pick another random point `D` on the terminal side, and draw "straight down" to point `E` of the initial side, we get a right triangle `∆ADE`.
 `∆ABC` and `∆ADE` are similar.
Property of similar triangle:
`(AB)/(AD) = (BC)/(DE) = (AC)/(AE)`
From this property we can get:
`(DE)/(AD) = (BC)/(AB)`
In other words, the ratio of the opposite side of `angle A` to the hypotenuse is a constant.
Mathematicians named this ratio sine(`sin`)
`∆ABC` and `∆ADE` are similar.
Property of similar triangle:
`(AB)/(AD) = (BC)/(DE) = (AC)/(AE)`
From this property we can get:
`(DE)/(AD) = (BC)/(AB)`
In other words, the ratio of the opposite side of `angle A` to the hypotenuse is a constant.
Mathematicians named this ratio sine(`sin`)