Newton's Second Law
`F = ma`
A net force acting on an object causes the object to accelerate in the direction of the force. 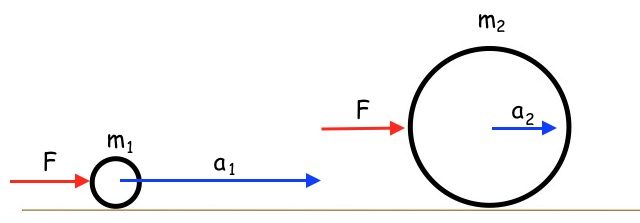 Mass is that property of an object that specifies how much resistance an object exhibits to changes in its velocity, the greater the mass of an object, the less that object accelerates under the action of a given applied force.
`m_1/m_2 = a_2/a_1`
Newton’s second law:
Newton’s second law states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass.
`sum vec(F)= m vec(a) `
(`sum vec(F)` is the net force)
Mass is that property of an object that specifies how much resistance an object exhibits to changes in its velocity, the greater the mass of an object, the less that object accelerates under the action of a given applied force.
`m_1/m_2 = a_2/a_1`
Newton’s second law:
Newton’s second law states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass.
`sum vec(F)= m vec(a) `
(`sum vec(F)` is the net force)
SI unit of force:
Newton (`N`)
Basic SI unit of force:
`kg•m//s^2`
