Weight on Earth
Gravitational force on an object near the Earth’s surface (weight).
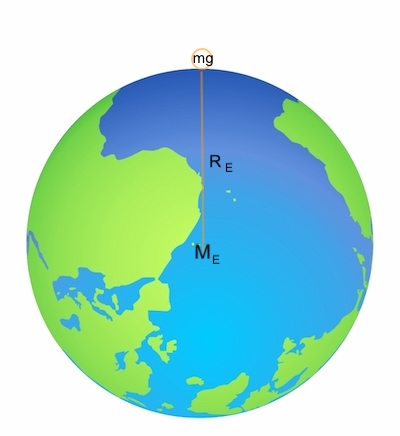

`mg = G (M_E m)/R_E^2`
`=>``g = G (M_E)/R_E^2`
The free-fall acceleration `g` to physical parameters of the Earth - its mass and radius - and explains the origin of the value of `9.80\ m//s^2` that we have used earlier. Now consider an object of mass `m` located a distance `h` above the Earth’s surface or a distance `r` from the Earth’s center, where `r = R_E + h`. The magnitude of the gravitational force acting on this object is
`F_g = G (M_E m)/r^2 =G (M_E m)/(R_E + h)^2`
`=>``g = G (M_E)/(R_E + h)^2`
Table of Free-Fall Acceleration `g` at Various Altitudes Above the Earth’s Surface:
